Encryption
Encryption is a way of scrambling data so that only authorized parties can understand the information. In technical terms, it is the process of converting human-readable plaintext to incomprehensible text, also known as ciphertext. In simpler terms, encryption takes readable data and alters it so that it appears random. Encryption requires the use of a cryptographic key: a set of mathematical values that both the sender and the recipient of an encrypted message agree on.
Symmetric Encryption
In symmetric-key encryption, the data is encoded and decoded with the same key. This is the easiest way of encryption, but also less secure. The receiver needs the key for decryption, so a safe way need for transferring keys. Anyone with the key can read the data in the middle.
Fernet
Steps
- Import Fernet
- Then generate an encryption key, that can be used for encryption and decryption.
- Convert the string to byte string, so that it can be encrypted.
- Instance the Fernet class with the encryption key.
-
Then encrypt the string with Fernet instance.
-
Then it can be decrypted with Fernet class instance and it should be instanced with the same key used for encryption.
from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
message = "Encrypt this message"
key = Fernet.generate_key()
fernet = Fernet(key)
# string must must be encoded to byte string before encryption
encMessage = fernet.encrypt(message.encode())
# Decrypting
decMessage = fernet.decrypt(encMessage).decode()
Asymmetric Encryption
In Asymmetric-key Encryption, we use two keys a public key and private key. The public key is used to encrypt the data and the private key is used to decrypt the data. By the name, the public key can be public (can be sent to anyone who needs to send data). No one has your private key, so no one the middle can read your data.
RSA
Steps:
- Import rsa library
- Generate public and private keys with rsa.newkeys() method.
- Encode the string to byte string.
- Then encrypt the byte string with the public key.
- Then the encrypted string can be decrypted with the private key.
- The public key can only be used for encryption and the private can only be used for decryption.
import rsa
publicKey, privateKey = rsa.newkeys(512)
message = "Encrypt this message"
# string must must be encoded to byte string before encryption
encMessage = rsa.encrypt(message.encode(), publicKey)
# Decrypting
decMessage = rsa.decrypt(encMessage, privateKey).decode()
Homomorphic Encryption
Python-Paillier
A Python 3 library implementing the Paillier Partially Homomorphic Encryption.
The homomorphic properties of the paillier crypto system are:
- Encrypted numbers can be multiplied by a non encrypted scalar.
- Encrypted numbers can be added together.
- Encrypted numbers can be added to non encrypted scalars.
Private Information Retrieval
using homomorphic encryption
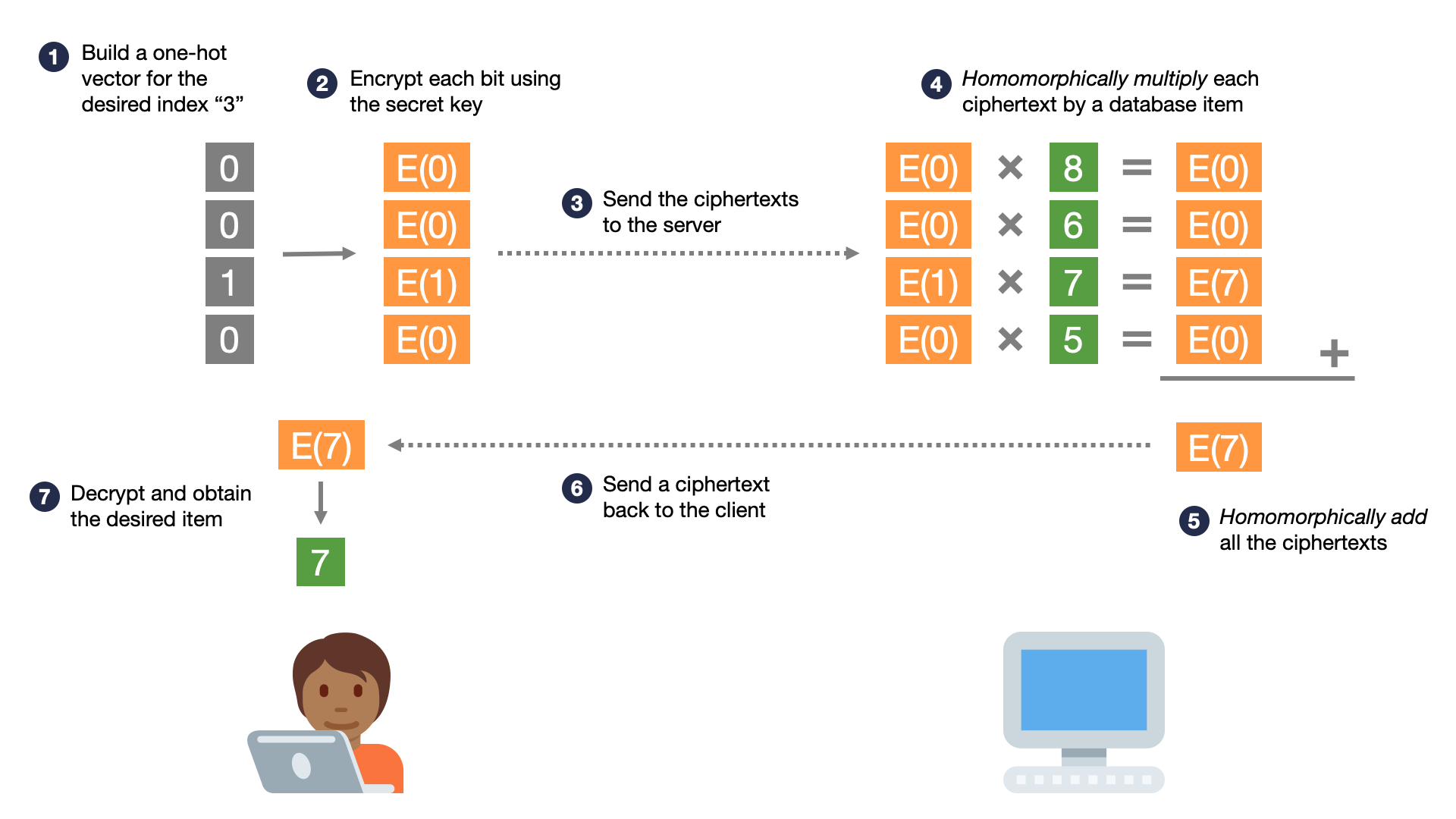
- The client encodes its desired index i=3i=3 in a one-hot encoding. That is, it builds a vector of n=4n=4 bits, where the ii-th bit is 11 and the rest are 00.
- The client generates a homomorphic encryption secret key, and uses it to encrypt each bit, producing nn ciphertexts, where the ii-th ciphertext is an encrypted 11, and the rest are encrypted 00's.
- The client sends this vector of encrypted bits to the server. To the server, this vector of encrypted bits is completely random noise; it cannot learn anything about the encrypted bits.
- The server takes the nn ciphertexts (each encrypting a bit), and homomorphically multiplies them by the corresponding plaintext database item. This produces a total of nn ciphertexts, each encrypting either 0 or the desired database item.
- The server homomorphically adds all of these ciphertexts, resulting in a single ciphertext encrypting the desired database item.
- The server sends this single ciphertext to the client.
- The client decrypts this ciphertext and obtains its desired plaintext item.
n = 512
q = 3329
noise_distribution = [-3, 3]
num_items_in_db = 50
desired_idx = 24
db = [random_bit() for i in range(num_items_in_db)]
def generate_query(desired_idx):
v = []
for i in range(num_items_in_db):
bit = 1 if i == desired_idx else 0
ct = encrypt(s, bit)
v.append(ct)
return v
def answer_query(query, db):
summed_A = zero_matrix(n, n)
summed_c = zero_vector(n)
for i in range(num_items_in_db):
if db[i] == 1:
(A, c) = query[i]
summed_A += A
summed_c += c
return (summed_A, summed_c)
s = keygen()
query = generate_query(desired_idx)
print("Sending the query to the server...")
answer = answer_query(query, db)
print("Got the answer back from the server...")
result = decrypt(s, answer)
print("The item at index %d of the database is %d", desired_idx, result)
assert result == db[desired_idx]
print("PIR was correct!")